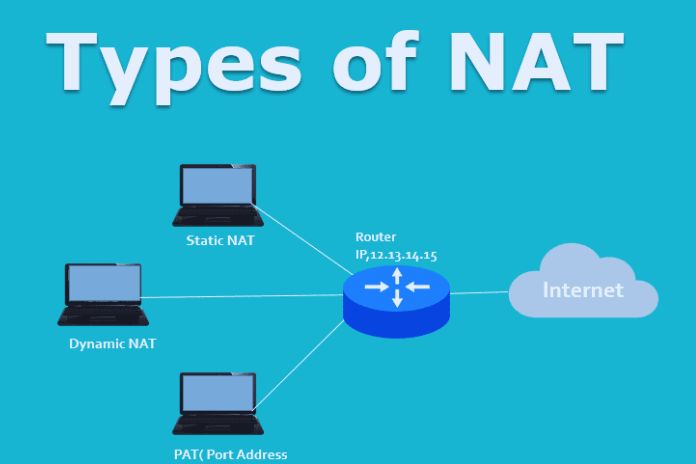
Types Of NAT: SNAT, DNAT, And PAT And Their Benefits And Cons
At the beginning of the Web, the “fathers” of Web planners considered involving 32 pieces for every IP address, believing that 4.2 billion accessible addresses were sufficient to cover any worldwide host. During the 80s, the Web was broad. For instance, the primary association with the Web through a PC occurred exclusively in 1986. From the 90s onwards, the Web has continually expanded new associations because of the advancement of the WWW and cell phones and information.
IPv4 addresses should have been more adequate to cover the developing number of gadgets in the organization. Moreover, the accessibility of 4,294,967,296 (or 2^32) is just a hypothetical number. The fundamental explanation for NAT innovation was to forestall the quick fatigue of IPv4 addresses. Network Address Interpretation (NAT ) permits an organization gadget (like a switch, firewall, or server running a working organization framework, for example, Windows 2008, Windows 2012, GNU Linux, or Unix) to decipher addresses between the public Web and a private neighborhood organization LAN.
How might this interpretation save the continually draining IPv4 addresses? The response is to utilize a confidential scope of IPv4 addresses. Predefined scopes of private IPv4 can design gadgets for private use (e.g., inside a corporate organization, home organization, in an organization, etc.). As such, traffic beginning in or bound for private IPv4 addresses can’t “leave” the secret organization.
This is the work done by the switch. This considers the reusability of private IPv4 trends across various confidential organizations. There is no IPv4 address struggle between two confidential IPv4 addresses isolated by NAT switch gadgets since private IPv4 addresses are converted into universally extraordinary public IPv4 addresses when they leave your organization. NAT permits a solitary, universally extraordinary IPv4 address to address a whole organization to the rest of the world.
Table of Contents
Let’s Get The Numbers: Private Ranges Of IPv4 Addresses
IPv4 address ranges are saved for private organizations (for instance, a corporate neighborhood (LAN) or a home organization). Each organization or subnet has a saved transmission address, which permits all organization members to send a comparing broadcast. This transmission address is if all host pieces are set to the parallel worth 1. If all host pieces are set to the value 0, it is the location of the comparing subnet.
Class A, range prefix: 10.0.0.0/8.
- Class A confidential IPv4 tends to begin from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255.
- 10.0.0.0/8 is the organization IPv4 address and 10.255.255.255 is the transmission IPv4 address.
- It consists of a sum of 16,777,216 IPv4 addresses. The Class A scope of private IPv4 addresses is utilized for enormous organizations that need a bigger pool of IPv4 addresses.
Class B, range prefix: 172.16.0.0/12.
- Class B private IPv4 tends to begin from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255.
- 172.16.0.0 is the IPv4 address of the organization (for the 172.16.0.0/16 organization) while 172.31.255.255 is the IPv4 communicated address for the 172.31.0.0/16 organization.
- It consists of a sum of 1,048,576 IPv4 addresses. The Class B scope of private IPv4 addresses is utilized for medium-sized networks.
Class C, range prefix: 192.168.0.0/16
- Class C confidential IPv4 tends to begin from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255.
- 192.168.0.0 is the IPv4 address of the 192.168.0.0/24 organization while 192.168.255.255 is the IPv4 communicated address for the 192.168.255.0/24 organization.
- It consists of a sum of 65,536 IPv4 addresses. The Class C scope of private IPv4 addresses is utilized for small organizations.
SNAT Extension
Static Network Address Translation or static NAT: This balanced planning between confidential IPv4 and public IPv4 addresses. Static NAT expects that you have a public IPv4 address for each confidential IPv4 address in your internal organization. Hence, IPv4 address conservation is beyond the possibilities of utilizing static NAT. The fundamental advantage of static NAT is that static NAT permits a PC in a small organization to start an association with a server inside the organization that is designed with a confidential IPv4 address.
Static NAT permits you to arrive at a server from inside your organization (designed with a confidential IPv4 address), like a web server or mail server, on the Web. The location interpretation idea of static NAT and dynamic NAT is comparative. Both static NAT and dynamic NAT interpret source/objective IPv4 addresses. The main distinction is that static NAT is a coordinated interpretation, and dynamic NAT is a many-to-one interpretation.
DNAT Extension
Dynamic Network Address Translation or Dynamic NAT: It very well may be characterized as the planning of a personal IP address to a public IP address from a gathering of public IP addresses called a NAT pool (it is a bunch of coterminous IP addresses, determined with a beginning IP address, a last IP address, and its subnet veil ). Dynamic NAT lays out coordinated planning between a personal IP address and a public IP address.
The public IP address taken from the IP pool tends to be arranged on the last NAT switch. People in general to-private planning can shift given the IP address in the NAT pool. When a secret organization PC sends an IP datagram to the outer organization, the DNAT gadget interprets the beginning IP address with a public IP address and advances it to the public organization.
PAT
Port Address Translation: This is another type of dynamic NAT that can map multiple private IPv4 addresses to a single public IP address using a technology known as Port Address Translation. Port address translation is also called NAT overhead. Port Location Interpretation (PAT/NAT Over-burden) is the NAT innovation that forestalls IPv4 address weariness. Port location interpretation (PAT/NAT over-burden) can plan secret IPv4 locations to a solitary public IP address utilizing different source ports.
In NAT over-burden, when a PC from an internal organization (designed with a confidential IPv4 address) speaks with one more PC on the Web, the NAT gadget (switch) changes the source port number (TCP or UDP) to one more number of ports. These TCP or UDP port mappings are stored in a table in the switch’s memory. Afterward, when the NAT gadget (switch) gets a reaction from the Web, the switch can utilize the table where port mappings are kept and forward the IPv4 information parcel to the first shipper.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of NATs
Network Address Translation (NAT) technology has many advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages Of NAT
- Can forestall weariness of IPv4 addresses (principal benefit).
- It can give an additional layer of safety by concealing the source and objective locations.
- Offers greater adaptability while interfacing with the public Web.
- Permits you to utilize your confidential IPv4 tending to framework and keep the inward location from changing if you change the specialist co-op.
Disadvantages Of NAT
- It is an asset and memory-consuming innovation, as Organization Address Interpretation (NAT) needs to decipher IPv4 addresses for all approaching and active IPv4 datagrams and keep the interpretation subtleties in memory.
- It can create setbacks for IPv4 correspondence.
- causes the deficiency of IP following the end gadget
- A few organization innovations and applications won’t fill in true to form in an Organization Address Interpretation (NAT) designed network.
Also Read: What Are Google Ads, And How Does It Work? Here You Can Know